Post link copied to clipboard!
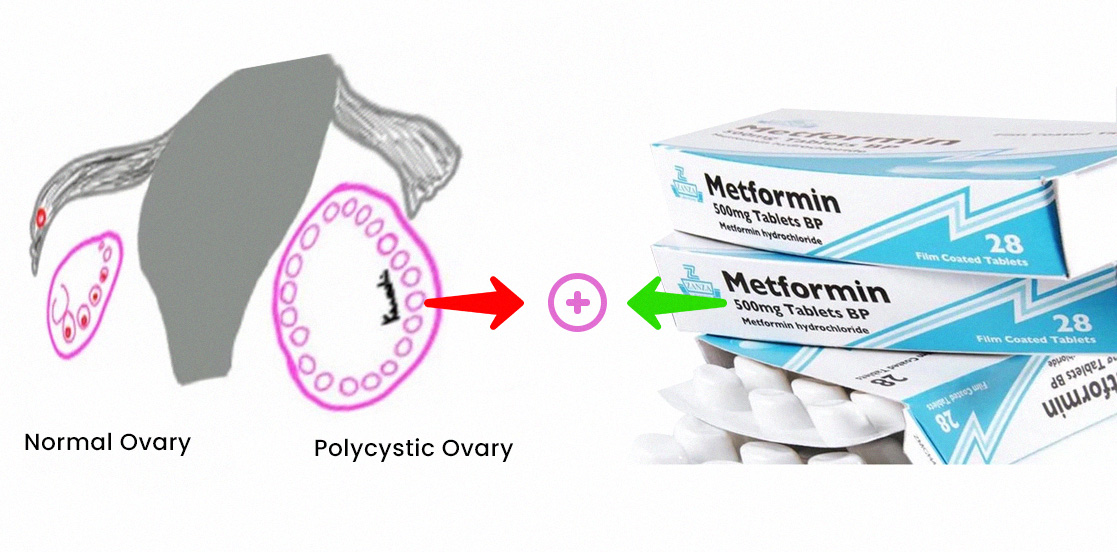
The most common medication used in women with PCOS is the insulin-sensitizer metformin.
Women with PCOS are commonly insulin resistant; their bodies can make insulin but can’t use it effectively, increasing their risk for type 2 diabetes. …
More than half of women with PCOS develop type 2 diabetes by age > 40 if they have weight issues.
Women with PCOS are more insulin resistant than weight matched women who do not have the syndrome.
Insulin resistance is seen in approximately 10% of slim and 40 % of obese women with PCOS
The more the overweight an individual is the greater the degree of insulin resistance .
Maternal weight can have a profound effect on both natural and assisted conception, influencing the chance of becoming pregnant and the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
As a result of insulin resistance in PCOS, circulating insulin levels rise. In the ovary, high levels of circulating insulin can contribute to excess male hormone production and to absent ovulation. Simple screening tests such as fasting blood glucose can help rule out the presence of insulin resistance, if it is less than 5.2 mmol/l, the risk of impaired glucose tolerance is low and the risk of developing gestational diabetes is low.
Metformin enhances sensitivity of insulin. Hence it is logical to anticipate that insulin lowering and insulin sensitising treatments, such as metformin, should improve symptoms and reproductive outcomes for women with PCOS. Metformin inhibits the production of sugar from the liver, decreases fat production, increases burning of the fat and inhibits new glucose molecule formation resulting in a decrease in circulating insulin and glucose.
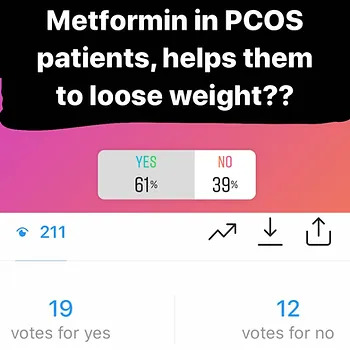
(Above is a short survey conducted on my instagram followers, majority are general public and are women, who have knowledge about PCOS and Metformin)
Metformin alone does not help to achieve weight loss in women with PCOS and Obesity. Therefore, lifestyle improvement and supporting women with individualised assessment, setting goals and using a combination of diet and exercise remains the first line approach. Once this approach has shown weight loss, then adding Metformin at that time has shown to be beneficial rather than starting Metformin as a sole agent to cause weight loss, which is not beneficial. In other words, a patient’s motivation to weight loss has to be established before starting Metformin by diet, exercise and will power.
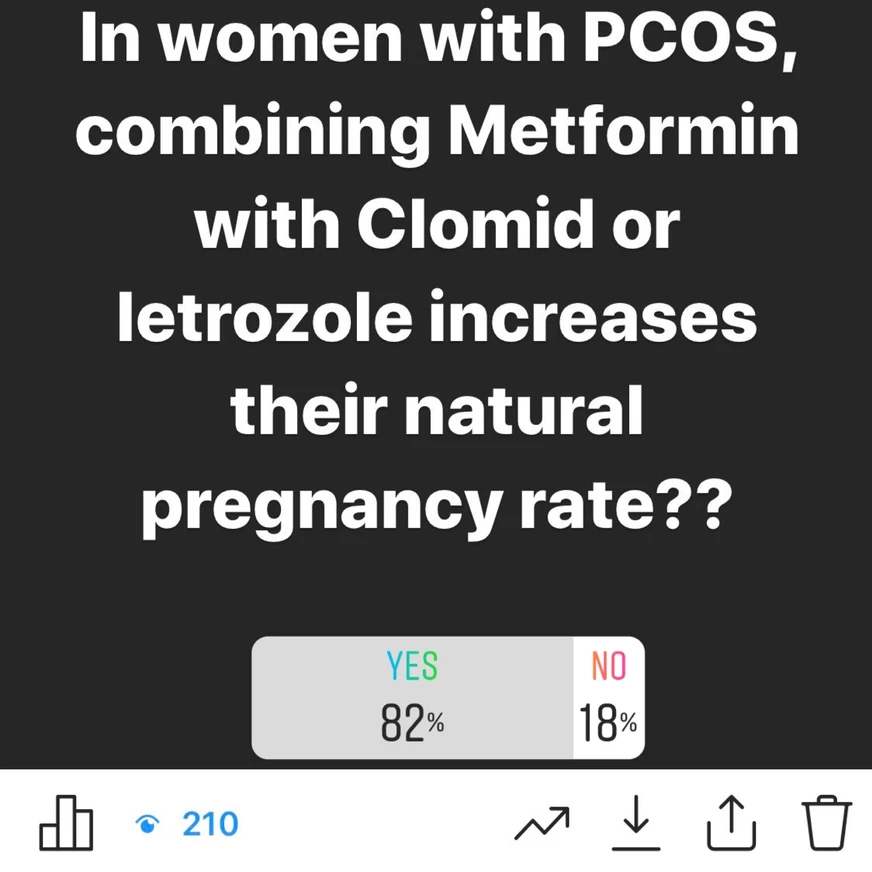
( Above is a short survey conducted on my instagram followers, majority are general public and are women, who have knowledge about PCOS and Metformin)
As first line therapy for the treatment of women who are anovulatory and infertile with PCOS,metformin alone was significantly less effective than clomiphene citrate alone.
Question : In women with PCOS, does combining Metformin with Clomid or Letrozole increase their natural pregnancy rate?
BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and of those with clomiphene citrate resistance may have a potential benefit from the combined use of metformin with clomiphene citrate
Question : I fell pregnant on Metformin, now, is it safe in early pregnancy?
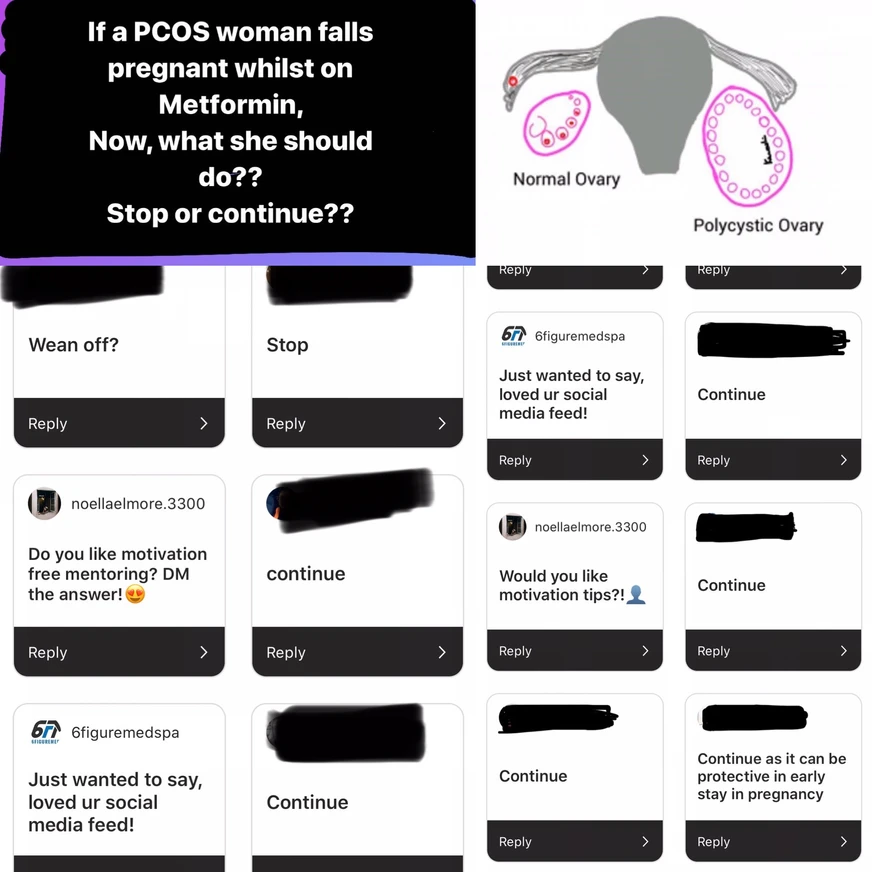
( Above is a short survey conducted on my instagram followers, majority are general public and are women, who have knowledge about PCOS and Metformin)
Metformin appears to be safe in pregnancy, however the usual advice is to discontinue post conception with the exception of those with existing diabetes
Metformin use can lead to unpleasant adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal bloating, diarrhoea, dizziness and unusual tiredness, 850 mg twice daily is the usual dose.
Women with PCOS who have not responded to clomiphene may be offered as a second-line treatment with Metformin.
One should be aware that there is a strong association between metformin treatment and decreased vit B12 levels in patients with PCOS, particularly women with weight issues and hyperinsulinemia.
Since the increase in a body chemical called Homocysteine could be due to the decrease in its essential cofactors (folic acid and vit B12) Research has shown that the long-term use of metformin at high doses (1500mg or higher daily for more than 6 months) can deplete levels of vitamin B12.
A deficiency of vitamin B12 can cause permanent neurological and nerve damage as well as mood changes and decreased energy.
The best absorbable form of Vitamin B12 is methlycobalimum. Taking vitamin B12 sublingual (under the tongue) is recommended. It is also recommended that patients who take metformin, have their vitamin B12 levels checked before the start of therapy and a year later.
Source :
Metformin Therapy for the Management of Infertility in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Scientific Impact Paper No. 13
First published: 23 August 2017
The role of metformin on vitamin B12 deficiency: A meta-analysis review
Article in Internal and Emergency Medicine 10(1):93-102 · February 2015
DOI: 10.1007/s11739-014-1157-5
Long-term Metformin Use and Vitamin B12 Deficiency in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016, doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3754. Epub 2016 Feb 22. 10.1210/jc.2015-375